When you’re out enjoying the beauties of our coast, it’s a good idea to know and understand the ocean, especially its tides since they vary depending on date, time, and location. Certain water activities can be challenging or even dangerous without knowledge of the tides. Whether you’re fishing, tide pooling, kayaking, or even just taking a stroll on the beach, it is always a good idea to know what to expect.
How Do Tides Work?
Tides are the rise and fall of the ocean’s surface water levels that vary with time and location. NOAA describes tides as long-period waves responding to the gravitational pull of the moon and sun. This large wave starts in the ocean and travels until it hits a coastline. When the highest part of the wave reaches the shore, high tide occurs. Low tide occurs when the dip in between waves reaches shore. High and low tides are generally about six hours apart.
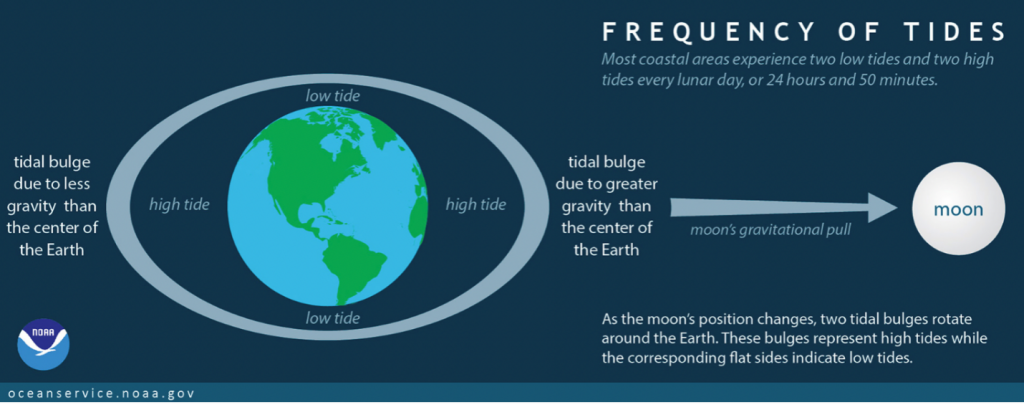
There are usually two high tides and two low tides per day. As the moon travels around the Earth, its gravitational force forms two points on the ocean’s surface, creating a shape almost like a football. These high points are called “tidal bulges.” The image above shows how the tidal bulges create the high tide, while the lower two sides are the low tide. As the moon moves around the Earth, the bulges shift, creating the daily pattern we see on our beaches and shorelines.
Tides are measured at local tide stations along the coast. Morro Bay gets its estimated tide times from the nearest station, which is at Port San Luis. Because of the distance between these two locations, the actual local tide times in Morro Bay may be slightly different than what is predicated for Port San Luis. It’s a common practice to use information from the nearest station for estimating tides.
How to Read a Tide Table or Graph
Tide tables contain important information, but they can be a bit confusing initially. Tide times can be in the format of a graph or a table. Both provide the height of the predicted high and low tides and the times they will occur during a 24-hour period.

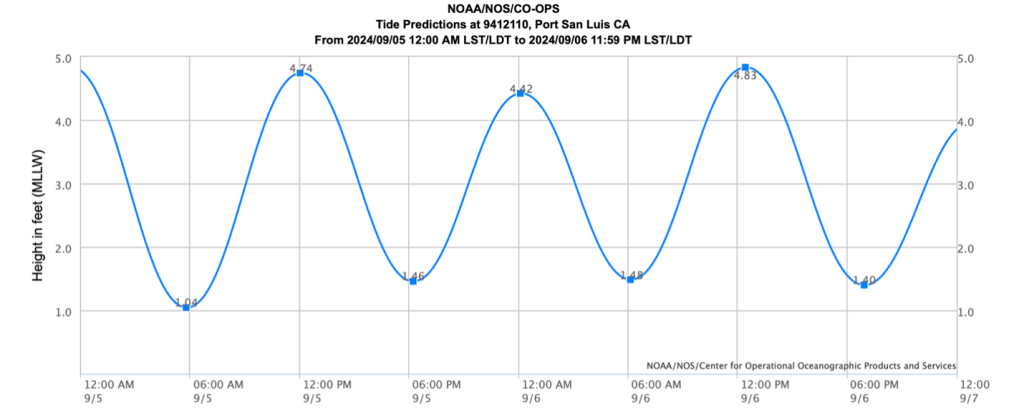
The Estuary Program provides Morro Bay tide tables that you can pick up at our Nature Center or at local events like farmer’s market. You can also find local tide times online at sites such as tidesandcurrents.noaa.gov and tide-forecast.com. Tide books most commonly use tide tables to represent tide times, while both tide charts and tables are found on websites.
How Tides Affect Morro Bay
The tides play a very important role in Morro Bay. The bay waters inundate and then recede, creating important ecosystems such as the mudflats and salt marsh communities that support a variety of species. They also affect many ocean recreation activities.
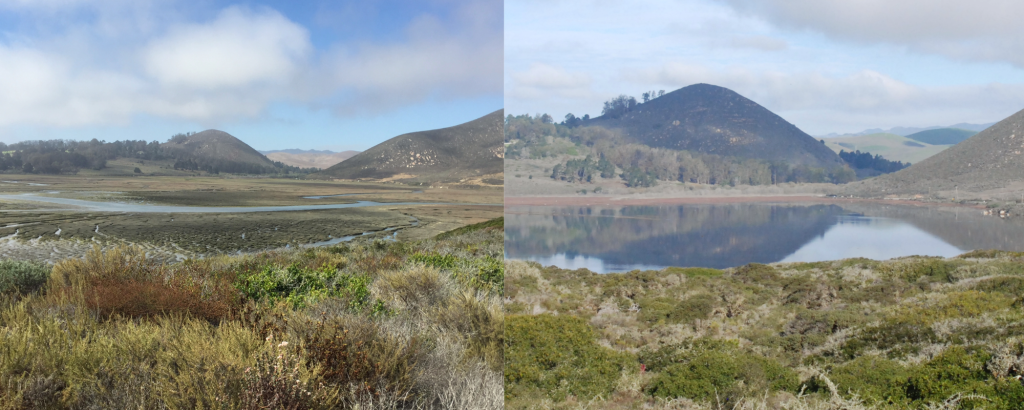

As seen in the photos above, there can be a drastic difference in conditions during low tides versus high tides. This large fluctuation in surface water levels creates a unique ecosystem for a variety of plant and animal species. Organisms that live in the salt marsh must be able to tolerate both full submergence in saltwater and full exposure to the air and sun. In addition, because the estuary does not get substantial freshwater input from the creeks during parts of the year, the tides play an important role in bringing in water, nutrients, and other important elements to these habitats.
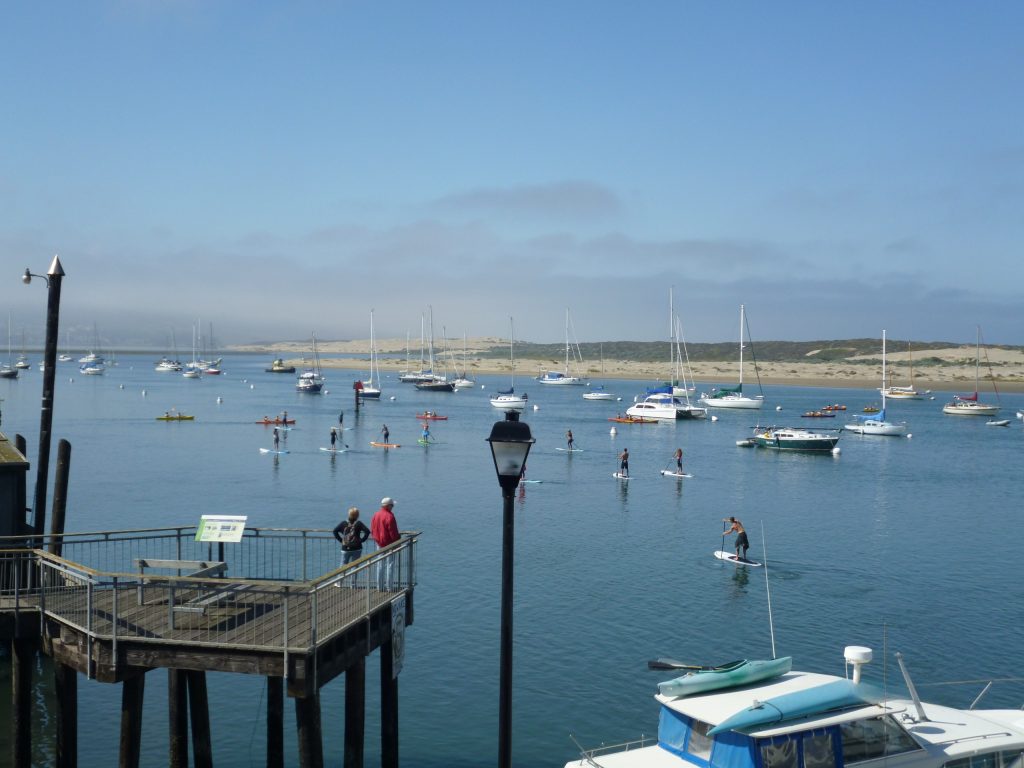

Tides also affect many recreational activities in Morro Bay, including boating, fishing, surfing, swimming, and even just going to the beach. Recreating in strong tidal currents can be risky, especially if participants are unaware of the changes in tides. Low tide could potentially result in boats running aground, especially in the back bay where the waters are shallow. High tide can cause beached kayaks to be swept away, stranding paddlers on the sandspit or beach. Awareness of the tides is essential for safety and to better plan your day’s activities. So whether you’re planning on tide pooling, paddling, swimming, or other adventures on or near the water, make sure to check the tides before heading to the coast.
Links
Help us protect and restore the Morro Bay estuary!
- Donate to the Estuary Program today and support our work in the field, the lab, and beyond.
The Estuary Program is a 501(c)3 nonprofit. As a result, we depend on funding from grants and generous donors to continue our work. - Support us by purchasing estuary-themed gear from ESTERO. This locally owned and operated company donates 20% of proceeds from its Estuary clothing line and 100% of Estuary decal proceeds to the Estuary Program. Thank you, ESTERO!
- Purchase items from the Estuary Program’s store on Zazzle. Zazzle prints and ships your items, and the Estuary Program receives 10% of the proceeds.
- Subscribe to our seasonal newsletter: Between the Tides!
- We want to hear from you! Please take a few minutes to fill out this short survey about what type of events you’d like to see from the Estuary Program. We appreciate your input!